C Tokens
C Tokens
Introduction
A programming language is designed to help process certain kinds of data consisting of numbers, characters and strings and to provide useful output known as information.
The task of processing data is achieved by writing instructions. These set of instructions is known as a program. Programs are written using words and symbols according to the rigid rules of the programming language known as syntax.
Character Set
The characters that can be used to form words, numbers and expressions depend upon the computer on which the program is run. The characters in C, are grouped into the following four categories:
1) Letters
2) Digits
3) Special Characters
4) Whitespaces
The compiler ignores the white spaces unless they are part of the string constants. White spaces are used to separate words from each other, but they cannot be used in between the characters of keywords and identifiers.
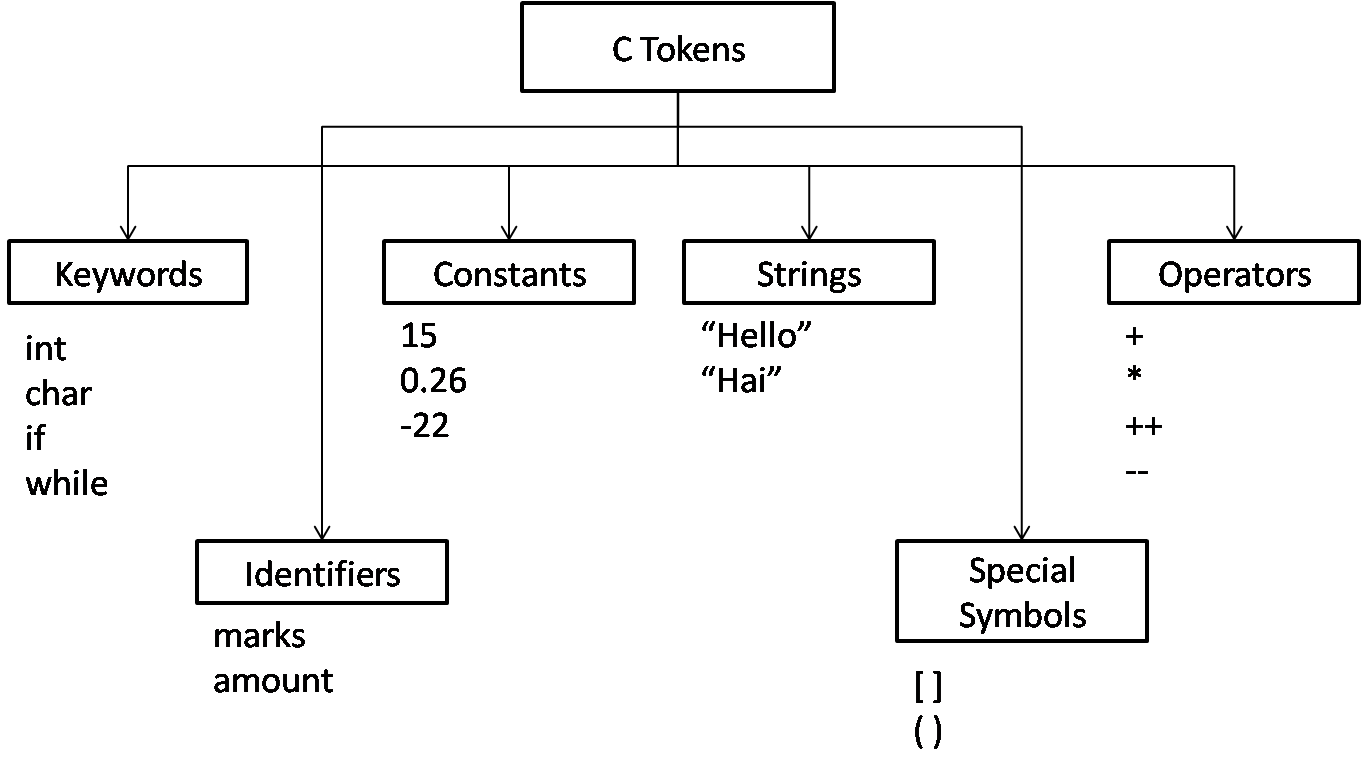
C Tokens
In a paragraph of text, individual words and punctuation marks are considered as tokens. Likewise in a C program, the smallest individual units are known as C tokens. C has six types of tokens as shown below. C programs are written using these tokens and the syntax of the language.
Keywords
Every word used in a C program is classified as either a keyword or as an identifier. A keyword in C is a reserved word which has a specific meaning. Keywords in C cannot be used as identifiers. Keywords serve as the basic building blocks for program statements.
Keywords in C are always in lowercase. ANSI C supports 32 keywords which are listed below:
Identifiers
Identifiers refer to the names of variables, functions and arrays. These are user-defined names and consist of sequence of letters and digits, with a letter as a first character. Both uppercase and lowercase letters can be used, although lowercase letters are generally used. The underscore character is also permitted in identifiers.
There certain rules while writing identifiers. They are as follows:
1) First character must be an alphabet or underscore.
2) Must consist of only letters, digits or underscore.
3) Only first 31 characters are significant.
4) Cannot use a keyword.
5) Must not contain white space.

Comments
Post a Comment